How to Choose the Best Thermal Graphite Film for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate Thermal Graphite Film is crucial for optimizing performance in various applications. With its unique properties, this advanced material has gained popularity across industries such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace, where efficient thermal management is essential. As manufacturers and engineers increasingly turn to Thermal Graphite Film to enhance heat dissipation, understanding the different types and specifications available becomes paramount.
In this guide, we explore key factors to consider when choosing the best Thermal Graphite Film for your specific needs. From thermal conductivity and thickness to the intended application and environmental conditions, making an informed decision can significantly impact the effectiveness of your thermal management solutions. Whether you are looking to improve the performance of a high-temperature electronic device or optimize the cooling efficiency of an automotive component, the right Thermal Graphite Film can make all the difference in achieving your performance goals.

Understanding Thermal Graphite Film and Its Applications
Thermal graphite film has emerged as a critical material in various applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. It is characterized by high thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1000 to 2000 W/m·K, making it ideal for electronics cooling, automotive components, and even in renewable energy systems. As the demand for miniaturization and performance enhancement in technology increases, understanding the properties and uses of thermal graphite film becomes essential.
According to a report by the Global Market Insights, the thermal management market is expected to reach over $25 billion by 2026, driven largely by advancements in electronic devices.
When selecting the best thermal graphite film for a specific application, it is crucial to consider factors such as thickness, thermal conductivity, and mechanical properties. For instance, a thicker film may provide better insulation but could compromise flexibility. Conversely, a thinner film tends to be more adaptable but might not meet the thermal requirements of high-performance applications.
Tips for selection include evaluating the thermal interface layers where the film will be applied and measuring the environmental factors, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations, that might affect performance. Additionally, partnering with suppliers that provide detailed thermal performance data can facilitate informed decision-making. Always ensure compatibility with your application’s specific needs to maximize efficiency and longevity.
Key Properties of Thermal Graphite Films to Consider
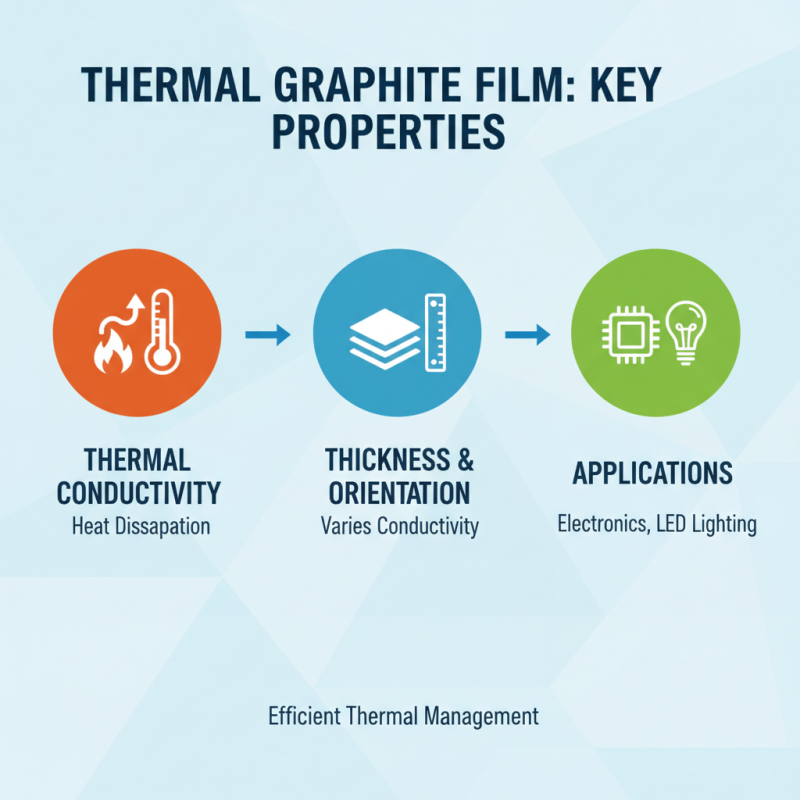
When selecting the best thermal graphite film for your specific application, understanding the key properties is crucial. One of the primary characteristics to consider is thermal conductivity, which significantly influences the film's ability to dissipate heat. Higher thermal conductivity values enable more efficient thermal management, making the film suitable for applications that involve high heat generation, such as in electronics or LED lighting. Additionally, the thermal conductivity can vary depending on the thickness and orientation of the graphite layers, so selection must align with the specific thermal requirements of your project.
Another important property to evaluate is mechanical flexibility. Some applications may require the thermal graphite film to conform to irregular surfaces or be integrated into flexible designs. Therefore, films with greater bending capabilities and tensile strength should be prioritized. Along with this, the film's adhesion properties are vital, especially in electronic devices where reliable bonding to substrates is essential for optimal performance. Furthermore, assessing the temperature stability and resistance to environmental factors will aid in choosing the right thermal graphite film that can withstand the operational conditions without degradation.
Factors Influencing the Selection of Thermal Graphite Films
When selecting a thermal graphite film for your application, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance. One of the primary considerations is thermal conductivity, as different applications may require varying levels of heat dissipation. High thermal conductivity is essential for electronics, where efficient heat management can prolong device life and enhance performance. It's advisable to evaluate the thermal conductivity specifications and select a film that matches the requirements of your specific use case.
 Another key factor is thickness, which can influence the film’s mechanical properties and flexibility. Thicker films generally provide better thermal management but may reduce conformability in tight spaces. Meanwhile, thinner films are more adaptable but may not offer the same level of heat dissipation. Therefore, it's important to assess the spatial constraints and design requirements of your application to determine the appropriate thickness.
Another key factor is thickness, which can influence the film’s mechanical properties and flexibility. Thicker films generally provide better thermal management but may reduce conformability in tight spaces. Meanwhile, thinner films are more adaptable but may not offer the same level of heat dissipation. Therefore, it's important to assess the spatial constraints and design requirements of your application to determine the appropriate thickness.
Additionally, factors like adhesion strength and environmental resistance play a crucial role; ensuring that the film adheres well to surfaces and can withstand the operating conditions will contribute to the longevity and effectiveness of the thermal management solution.
Applications and Industries Benefiting from Thermal Graphite Films
Thermal graphite films are revolutionizing various industries by providing superior thermal management solutions. In electronics manufacturing, these films are crucial in dissipating heat in devices such as smartphones, laptops, and LED lights, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By efficiently conducting heat away from critical components, thermal graphite films help maintain operational efficiency and reduce the risk of overheating, which can cause performance degradation or failure.
Beyond electronics, thermal graphite films are also increasingly adopted in the automotive sector. They play a vital role in thermal interfaces and battery management systems, particularly in electric vehicles. As the need for effective thermal regulation in batteries becomes more important for enhancing safety and performance, these films provide a lightweight and effective solution. Similarly, in the renewable energy industry, such as solar panels, thermal graphite films enhance energy efficiency by improving heat management, leading to better overall performance and reliability of the systems.
Comparative Analysis of Thermal Graphite Films and Alternatives
When selecting a thermal interface material for specific applications, understanding the comparative performance of thermal graphite films versus alternative materials is crucial. According to a market analysis report by MarketsandMarkets, the global thermal interface materials market is projected to reach USD 3.4 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.4%. This growth indicates an increasing demand for efficient thermal management solutions in various industries, including electronics, automotive, and HVAC.
Thermal graphite films are often favored due to their exceptional thermal conductivity and thin profile, making them suitable for applications that require advanced heat dissipation. For example, the thermal conductivity of high-quality graphite films can exceed 1000 W/m·K, significantly outperforming traditional materials like thermal pads or silicones, which generally have thermal conductivities ranging from 1 to 20 W/m·K. This distinction is critical as it allows devices to operate at optimal temperatures, enhancing performance and extending lifespan.
In contrast, while some alternatives may offer benefits such as lower cost or easier application, they often fail to provide the same level of thermal efficiency. A report from IDTechEx also notes that innovative materials like phase change materials (PCMs) can effectively manage heat by absorbing and releasing thermal energy. However, they typically require more space and may not achieve the rapid thermal response that products based on thermal graphite films can deliver. This positioning underscores the importance of evaluating both the thermal performance and the physical characteristics of these materials when making decisions for specific applications.
Comparative Analysis of Thermal Conductivity of Graphite Films and Alternatives
Related Posts
-

China's Leading Edge: The Evolution of the Best Graphite Thermal Sheets in Global Manufacturing
-

5 Innovative Ways the Best Graphite Cooling Film Can Transform Your Technology
-

What Makes Graphite Sheets the Ideal Choice for Industrial Applications
-
How to Choose the Right Graphite Thermal Sheet for Your Application
-
Unlocking the Potential of Thermal Graphite Film in Modern Electronics
-
Top 10 Benefits of Graphite Gasket Sheets You Should Know About